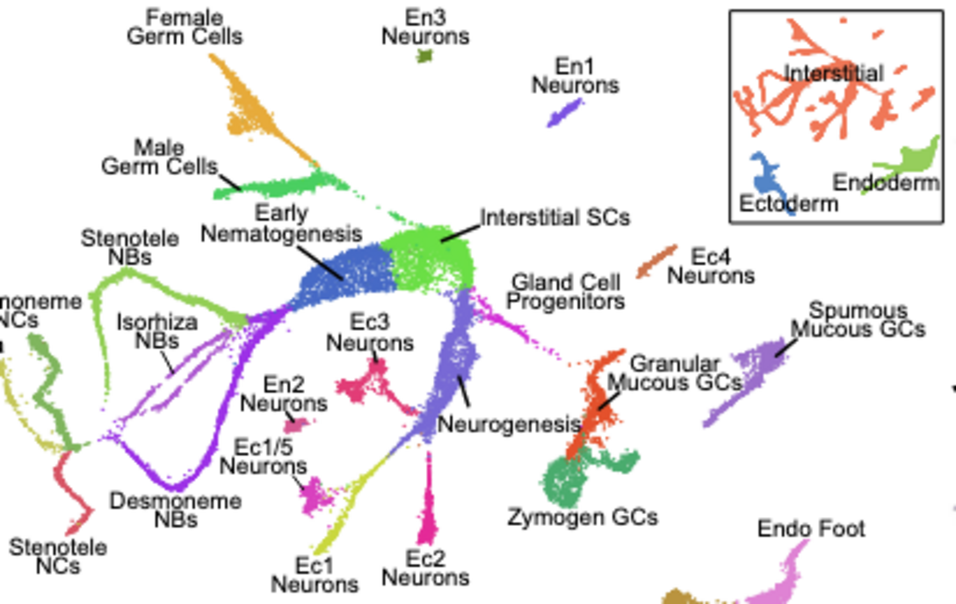
The epithelial and interstitial stem cells of the freshwater polyp Hydra are the best characterized stem cell systems in any cnidarian, providing valuable insight into cell type evolution and the origin of stemness in animals. However, little is known about the transcriptional regulatory mechanisms that determine how these stem cells are maintained and how they give rise to their diverse differentiated progeny. To address such questions, a thorough understanding of transcriptional regulation in Hydra is needed. To this end, we generated extensive new resources for characterizing transcriptional regulation in Hydra, including new genome assemblies for Hydra oligactis and the AEP strain of Hydra vulgaris, an updated whole-animal single-cell RNA-seq atlas, and genome-wide maps of chromatin interactions, chromatin accessibility, sequence conservation, and histone modifications. These data revealed the existence of large kilobase-scale chromatin interaction domains in the Hydra genome that contain transcriptionally co-regulated genes. We also uncovered the transcriptomic profiles of two previously molecularly uncharacterized cell types, isorhiza-containing nematocytes and somatic gonad ectoderm. Finally, we identified novel candidate regulators of cell-type-specific transcription, several of which have likely been conserved at least since the divergence of Hydra and the jellyfish Clytia hemisphaerica over 400 million years ago.